Publications
Articles, publications, books, tools and multimedia features from the U.S. Institute of Peace provide the latest news, analysis, research findings, practitioner guides and reports, all related to the conflict zones and issues that are at the center of the Institute’s work to prevent and reduce violent conflict.
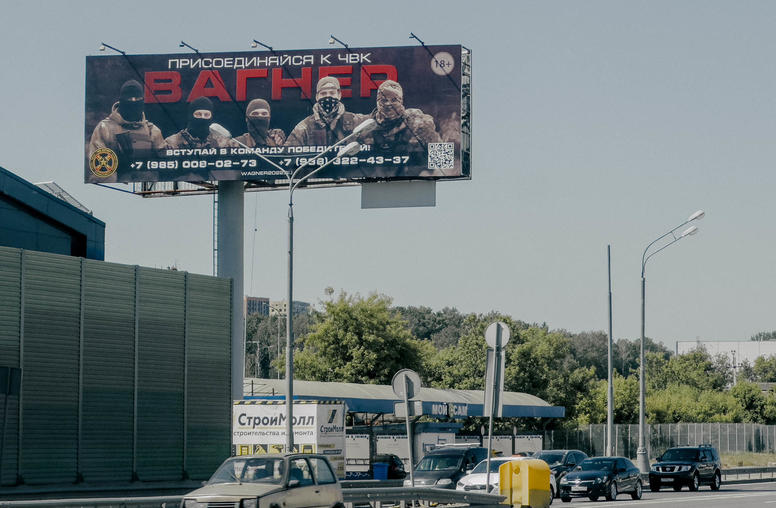

Russia’s Africa Summit — and a Future for Wagner
Ever since Russia’s Wagner mercenary group jolted Vladimir Putin’s regime with its brief mutiny in Russia, foggy uncertainty has surrounded Wagner’s future roles — whether domestically, as part of Putin’s web of armed forces, as a fighting force in Ukraine, or as a Kremlin tool of influence and profit in Africa. The past week offers the most prominent sign yet of how Wagner’s flamboyant chief, Yevgeniy Prigozhin, is pressing to retain an African role. While mostly shoved out of public view, Prigozhin was able to appear at Putin’s Russia-Africa Summit to meet African contacts and re-declare his relevance.
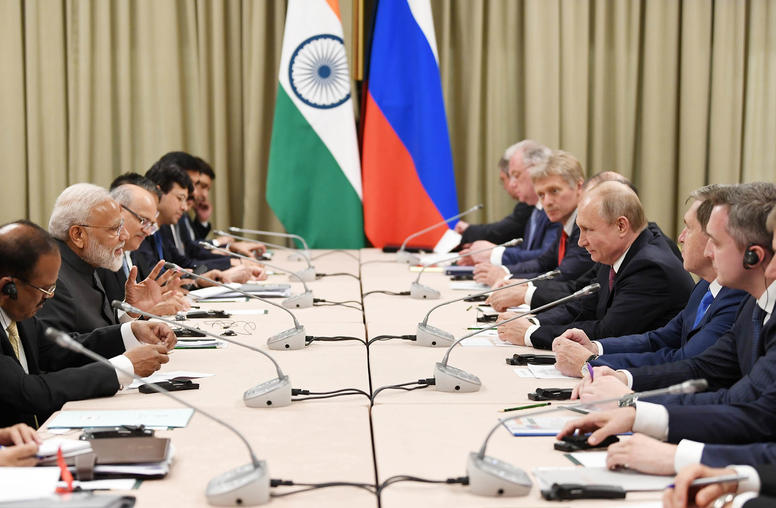

The Limitations of India and Russia’s Transactional Relationship
Since Russia’s unprovoked invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, it might seem as though ties between India and Russia have strengthened. While much of the West isolated Russia, India-Russia energy trade spiked, and India made efforts to accommodate Russia on the world stage. The two countries have also had visible public exchanges, such as a mid-January phone call between Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Russian President Vladimir Putin and Indian External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar’s trip to Moscow at the end of 2023.
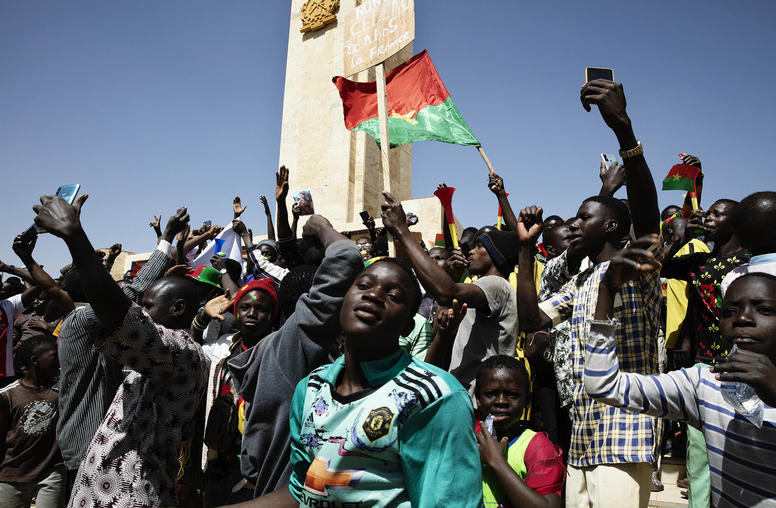
For Peace in Sahel, African and U.S. Experts Urge Focused Partnership
The past month has sharpened a decade-old question for U.S. and international policymakers: How best, in 2024, to help stabilize what is now the world’s largest single zone of military rule and violent conflicts — Africa’s Sahel region? After three military-ruled Sahel states withdrew from the West African regional community in January, those juntas last week proclaimed an alliance aimed at resisting international pressures, including those for their return to elected civilian rule. Former U.S. and African officials yesterday urged what they called vital changes in U.S. and allied policies to prevent a dangerous spread of the Sahel’s crises.

Thomas Sheehy on U.S. Investment in Africa’s Critical Minerals Infrastructure
Everything from the economy to national security depends on critical minerals like cobalt — which has prompted immense U.S. investment in Africa’s mining infrastructure, says USIP’s Thomas Sheehy: “Africa is seen as a continent where we can start to very slowly move away from our overdependence on China for critical minerals.”
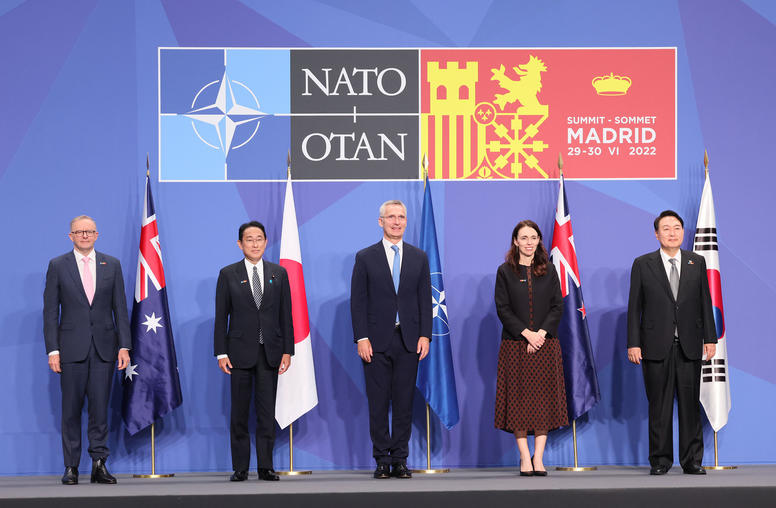

Report of the Expert Study Group on NATO and Indo-Pacific Partners
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and its four partner countries in the Indo-Pacific—Australia, Japan, the Republic of Korea (ROK), and New Zealand—have entered a period of increased engagement. This engagement is taking shape in the context of the war waged by the Russian Federation (Russia) against Ukraine, NATO’s growing awareness of the security challenges posed by the People’s Republic of China (China), and important structural changes in the international system, including the return of strategic competition between the United States and China and Russia. It is occurring not only in bilateral NATO-partner relations but also between NATO and these Indo-Pacific countries as a group.
Senior Study Group for the Sahel: Final Report and Recommendations
The United States has not traditionally viewed the Sahel as a region of vital interest, whether in terms of security or from an economic or business perspective. This has led to a pattern of reactive involvement shaped by the circumstances of specific events rather than proactive commitments. This pattern reveals the lack of a comprehensive strategy for the volatile Western Sahel region, which includes Burkina Faso, Chad, Mali, Mauritania, and Niger. In April 2022, President Joe Biden announced that the US government would advance the “U.S. Strategy to Prevent Conflict and Promote Stability” in coastal West Africa by prioritizing a partnership with Benin, Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, Guinea, and Togo.
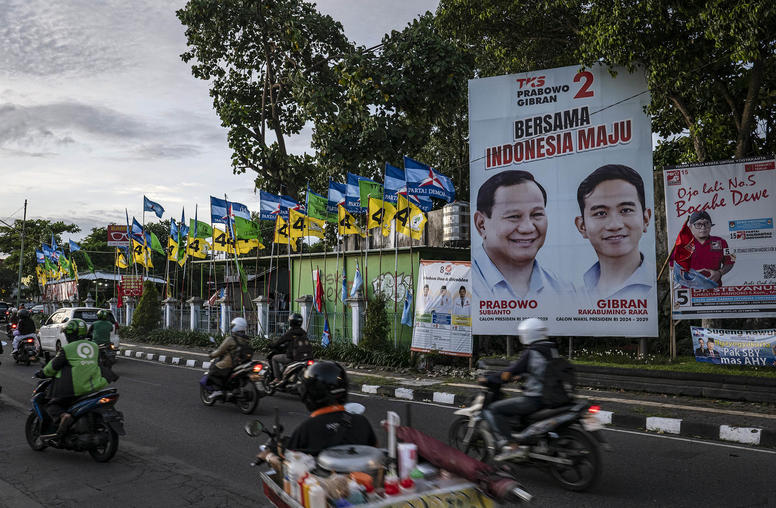

How Might Prabowo Navigate Conflict, Competition as Indonesia’s President?
Indonesia’s defense minister, Prabowo Subianto, is set to become the next president of the world’s fourth-largest country and third-largest democracy. Prabowo will take the reins of power at a tense moment for regional and global security and as president will have to contend with a persistent, low-grade conflict in West Papua. Continuity will likely hold sway as prevailing winds in Indonesia’s foreign policy chart a well-worn course for navigating geopolitical competition and global conflicts, this time with what appears to be a willing captain at the helm.
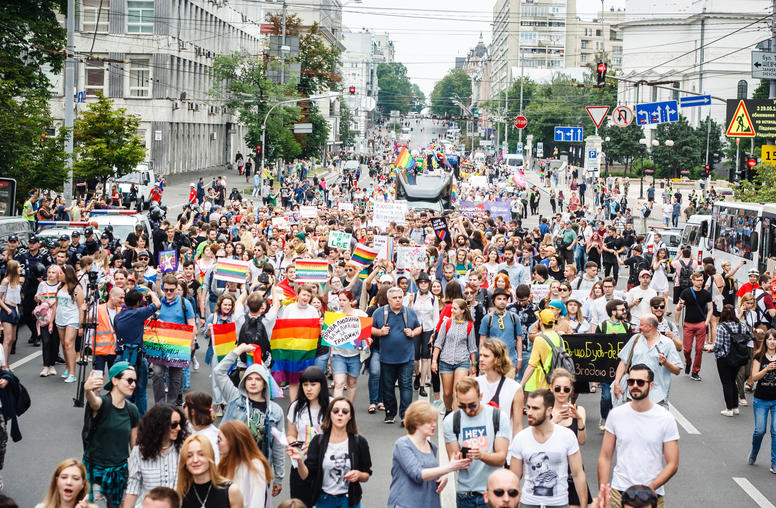

A Democratic Ukraine Must Include All LGBTQ+ People
As Ukraine fights for survival, it has relaxed some barriers to the social inclusion of gay, lesbian and other gender and sexual minorities—for example, welcoming some gay people into its armed forces. Yet this change should be expanded and made permanent. Often countries recruit marginalized minorities during wartime emergencies only to revive old practices of exclusion in peacetime. The more inclusive democracy that Ukraine aspires to, and that its transatlantic allies support bringing into full membership of Europe, will require transformations in laws, institutions and social norms for the equal inclusion of Ukrainian gender and sexual minorities.
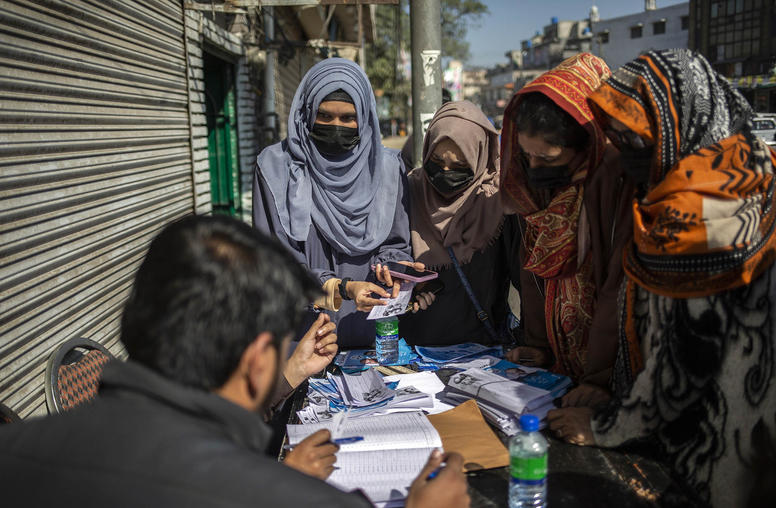

Understanding Pakistan’s Election Results
Days after Pakistan’s February 8 general election, the Election Commission of Pakistan released the official results confirming a major political upset. Contrary to what most political pundits and observers had predicted, independents aligned with former Prime Minister Imran Khan’s Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) won the most seats at the national level, followed by former Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif’s Pakistan Muslim League-Nawaz (PML-N), the Pakistan Peoples Party (PPP) and the Muttahida Qaumi Movement (MQM). No party won an absolute majority needed to form a government on its own. The resultant uncertainty means the United States may have to contend with a government that is more focused on navigating internal politics and less so on addressing strategic challenges.
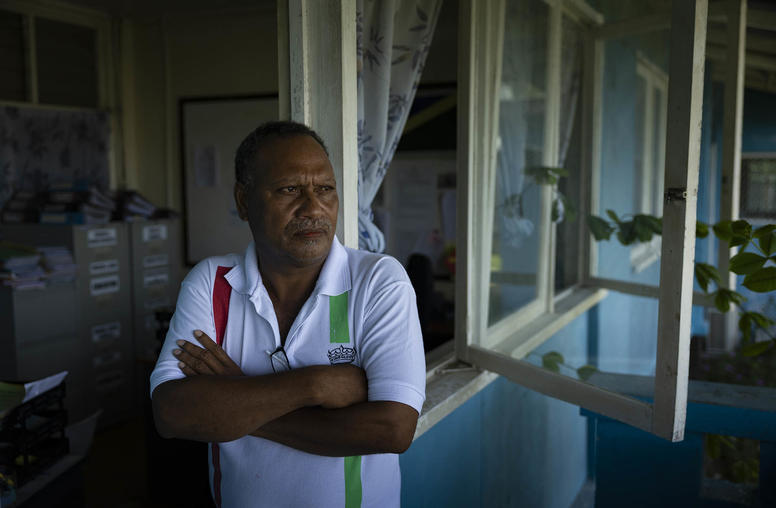

Malaita and the Provincial-National Divide in Solomon Islands
In 2019, Malaita Province in Solomon Islands made geopolitical headlines when its former premier, Daniel Suidani, came out against the country’s closer bilateral relations with China. As a result of his stance, Suidani was removed from his position in February 2023.